Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease in which the vertebrae and intervertebral discs are affected. Cervical osteochondrosis refers to deforming dorsopathies. Involutionary changes in the disks were observed as early as the 20th year. At the same time, they become more sensitive to loads, less elastic and lose lubricating fluid.
The pathology most often occurs in the elderly, but there is currently a significant increase in incidence among children and adolescents. Neurologists identify cervical osteochondrosis using the latest diagnostic studies. After clarifying the diagnosis, complex therapy is carried out with the most effective drugs, physiotherapy procedures and innovative methods of physical rehabilitation.
The name of the disease consists of two Greek terms "osteon" (bone) and "chondros" (cartilage). Cervical osteochondrosis begins with changes in the central part of the disc. The intervertebral disc loses moisture, decreases in size, which leads to convergence of the vertebral bodies and disruption of nerve roots with vessels. The vertebrae receive nutrients from the surrounding tissues, which is harmful to the body. Compression of nerves and blood vessels leads to a protective muscle spasm, which, as the disease progresses, becomes the cause of pain.

Which doctor treats this disease
Treatment of osteochondrosis is the area of activity of neurologists. However, when symptoms of neck osteochondrosis appear, it is possible to consult a general practitioner. The neurologist will select medications for cervical osteochondrosis that have the least stress on the body, which is important for drug therapy.
In order to determine the presence of a pathological process in the cartilage tissue and cervicobrachial osteochondrosis, the patient is referred for a comprehensive examination. Tactics for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis are being developed in accordance with the results of research.
Interdisciplinary collaboration also allows for the treatment of concomitant diseases that the patient has. In addition, the patient receives full informative support: treatment plan, statement of service costs, provision of information on specialist consultations and diagnostic measures.
Causes
Cervical osteochondrosis develops under the influence of various provoking factors. The definitive cause of cervical osteochondrosis has not been determined. The disease is often associated with metabolic disorders and aging of the vertebrae.
Researchers suggest that cervical osteochondrosis develops for the following reasons:
- Excessive stress on the spine. A high load on the spine is noticed when wearing the wrong shoes, flat feet, obesity, prolonged sitting;
- Metabolic disorders. Lack of vitamins, minerals, disorders of calcium metabolism can serve as causes of degenerative processes in the vertebrae;
- Congenital and acquired anomalies of the spine and ligament apparatus (ligament thickening, lumbarization, sacralization);
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to insufficient absorption of nutrients;
- Infection, intoxication;
- Injuries, bruises, fractures of the spine, resulting in disruption of blood supply and innervation of the spine, causing their dystrophic disorders;
- Stress;
- Wearing shoes with heels;
- Pregnancy, especially multiple;
- Autoimmune connective tissue lesions, abnormal collagen type 1 and 2 structure;
- Occupational hazards (lifting heavy loads, prolonged vibration, working in a sitting position with a constant tilt of the head);
- Atherosclerotic and other changes in the spinal arteries;
- Curvature of the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis, kyphoscoliosis).
An important risk factor for the development of cervical osteochondrosis is burdened heredity. This fact proves the presence of osteochondrosis in children, when the spine is not overloaded yet.
Degrees
Thanks to the special structure of the spine, it is able to perform its functions. The main structural unit is considered to be the spinal movement (VMS) segment. It consists of two adjacent vertebrae, the intervertebral disc and the musculo-ligament apparatus. Osteochondrosis leads to dystrophic-degenerative processes, first in the intervertebral disc, then in the vertebrae. With the defeat of one vertebra, the performance of its functions is ensured by the neighboring ones. This leads to an increase in load and loss of mobility of the affected segment.
In the development of cervical osteochondrosis, doctors distinguish several stages:
- First degree cervical osteochondrosis. Because the intervertebral disc is deprived of its own blood supply and receives nutrients from the surrounding tissues, it is subject to degenerative changes. Osteochondrosis in the 1st stage of development is characterized by the destruction of the nucleus pulposus and cracks in the annular fibrosus. Clinically, this is manifested by acute or persistent local neck pain (cervicalgia) and stiffness;
- Second-degree osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. At this stage, the destruction of the annular fibrosus continues, pathological motility and instability of the vertebrae appear. Patients complain of neck pain, intensified by physical exertion, tilting the head or in a certain position;
- The third stage of the disease is characterized by the complete destruction of the annular fiber. The gelatinous core is not fixed. A disc herniation can occur and cause severe pain. At this stage, due to poor SMS fixation, a curvature of the spine can be created;
- In the fourth stage of the disease, the intervertebral disc is replaced by connective tissue, and other adjacent segments are affected. Spondyloarthritis, arachnoiditis, develops. The joints become completely immobile - ankylosis develops. Bone tissue grows around the affected area - osteon is formed. In the fourth degree of cervical osteochondrosis, vivid symptoms are noticed: severe pain radiating to the arm, sternum, in the area between the shoulder blades, sensitivity disorders.

Symptoms and signs
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis in the initial stages may be non-specific: dizziness, headache, weakness, crunch during head movements. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms develop:
- Severe pain in neck and shoulders;
- Numbness of the hand;
- Dizziness;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Increased sweating.
There are several syndromes that occur with the development of a pathological condition of the muscles of the back and cervical spine:
- Cervical migraine syndrome.
- Vertebral artery syndrome.
- Hypertensive syndrome.
- Cardiac syndrome.
- Radicular syndrome.
They occur when nerve endings, constricted arteries and veins are injured during the development of the disease. The most dangerous complication is considered to be the vertebral artery syndrome. There is a violation of blood flow through the artery that feeds the brain and spinal cord. The patient reduces hearing, vision decreases, and constant dizziness develops. The patient may lose consciousness while driving due to a sharp violation of blood flow.
As a result of compression of the nerves responsible for innervation of the chest muscles and diaphragm, pain appears in the area of the heart, which is not related to heart disease, but at the same time, tachycardia, arrhythmia and hypotension can develop. Vein compression leads to the development of hypertensive cerebrospinal fluid syndrome. Intracranial pressure increases, nausea, vomiting and severe headache occur due to impaired blood flow to the brain.
As a result of neck tightening, a radicular syndrome develops - severe pains appear in the neck, shoulders, shoulders and back of the head. With this syndrome, the arm and neck area becomes numb. With cervical migraine syndrome, the patient is concerned about severe pain in the back of the head, which is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Reflex syndromes occur when the spinal roots are not yet affected. Patients complain of pain in the neck, head (especially the back of the head), hands on one or both sides. Reflex pain, unlike radicular pain, is not combined with sensitivity disorders. Cervical pain can be dull, painful. A sharp sharp pain in the lumbago is called cervicago. There is cramping and pain in the muscles, pain in the paravertebral points. Signs of cervical osteochondrosis intensify in an awkward position, with tilting of the head, coughing, physical exertion. Signs of epicondylosis, humeroscapular periarthrosis, and shoulder-arm syndrome occur due to nerve impulses from the annular fibrosus of the affected segment, causing compensatory muscle spasm.
Radicular syndromes are accompanied by impaired motor activity and sensitivity. At the same time the nerves, blood vessels are damaged, venous and lymphatic outflow in the pathological focus is disturbed as a result of the reduction of the intervertebral canal. The pain in radicular syndrome is acute, intense. A common cause of spinal nerve entrapment is the formation of a hernia. In the area of pathological focus, muscle tone decreases. In radiculoischemia, in addition to the nerves, the vessels also constrict.
If the phrenic nerve is involved in the pathological process, cardiac syndrome occurs. It manifests as a burning, acute pain in the left side of the chest with irradiation to the arm, the interduloid region. The name of the syndrome is due to the fact that the nature of the pain is similar to an attack of angina pectoris. The main difference between the pains of angina pectoris is that they are relieved after taking nitroglycerin, can occur at rest and are combined with cardiac arrhythmias (tachycardia, arrhythmia).
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis depend on the localization of the pathological process. Damage to the upper cervical vertebrae disrupts the supply of the brain due to compression of the cerebral arteries. This leads to headache (especially in the occipital region), dizziness, fainting, high blood pressure. Dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis is caused by reduced blood flow in the inner ear. Patients are also concerned about nausea, vestibular and ocular symptoms occur.
With a combined vertebral lesion, they speak of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Dizziness;
- Neck and arm pain;
- Tingling, a feeling of crawling on the upper limb;
- Intercostal neuralgia.
Diagnosis
Cervical osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that can lead to the formation of hernias and compression of the spinal cord. Therefore, it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis in time and start therapy. The following types of instrumental diagnostics are used to recognize cervical osteochondrosis:
- Spondylography or X-ray of the spine. This research method is painless, highly informative and does not require special training. X-ray of the spine enables the assessment of its anatomical and functional characteristics. The picture pays attention to the structure of the vertebrae, their mutual relationship, the distance between them, the lumen of the spinal canal;
- Computed tomography - provides information mainly on the condition of bone tissue, allows you to identify narrowing of the spinal canal and herniated disc;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to detect changes in soft tissues. MRI image clearly shows changes in the intervertebral discs and spinal cord.

Drug treatment
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine consists of drug therapy and non-drug medications. Even after complete cure, neurologists implement preventive measures to rule out relapses of the disease. In the acute period, for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, doctors prescribe drugs to patients of the following pharmacological groups:
- Inorganic analgesics. They are taken orally or injected intramuscularly to achieve the effect quickly;
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- B vitamins in large doses.
Diuretics are used to reduce fluid retention in the spinal root and surrounding tissues. Antihistamines enhance the action of analgesics. Muscle cramps are removed with muscle relaxants. With prolonged severe pain syndrome, neurologists perform nerve blockade.
Chondroprotectors are used to improve metabolic processes in the intervertebral disc. These drugs increase the content of glycosaminoglycans, increase the strength, elasticity and absorption of shocks on the intervertebral discs.
Dizziness tablets
Patients often experience dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis. To reduce them, doctors prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. NSAIDs belonging to different groups differ in mechanism of action and action, so only a qualified specialist can determine the appropriate drug.
It is important to remember that medications for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine cannot be taken without a doctor's appointment. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have side effects, so before prescribing them, the neurologist determines the presence of contraindications in the patient and the required dose. Medications for vertigo in cervical osteochondrosis can improve a patient’s quality of life.
Injections for osteochondrosis
Injections for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine help relieve pain during exacerbations. With this method of drug administration, the effect occurs quickly. Neurologists use a variety of injections.
Nurses inject drug solutions subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously. In the period of worsening of the disease, drugs given by injections, with cervical osteochondrosis, have an exclusively symptomatic effect.
Headache treatment
Headache is a symptom that occurs in various disorders. However, cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by attacks of intense headache. Head movements intensify the symptoms, therefore, to eliminate them, doctors prescribe analgesic pills and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Drug-free therapy methods
Complex non-medical therapy of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine includes:
- Protective mode - when the roots are tightened, patients lie on a hard surface,
- Massage;
- Physiotherapy exercises;
- Pulling the spine;
- Physiotherapy procedures.
Massage for cervical osteochondrosis is used to reduce pain and swelling, improve peripheral blood supply and eliminate muscle spasms. Contraindication for performing this procedure is the presence of acute pain. Massage the neck and back in the direction of lymph outflow. Special attention is paid to the interscapular and paravertebral zone.
Therapeutic gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine aims to eliminate muscle spasms and strengthen the muscular frame. Because vertebral instability often occurs in the cervical spine, the exercise therapy instructor performs individual lessons during which he teaches the patient to perform the exercises safely. Some authors recommend teaching physical therapy in a Shants necklace.
To improve the mobility of the cervical spine, rehabilitation therapists recommend performing the following exercises:
- Bending and extension of the door. Tilt your head toward your sternum, without pulling your shoulders forward and then back. Hold the slope for 3 seconds, repeat each exercise 8-10 times;
- Turn the door. Turn the neck first to the left until it stops, and then to the right, without changing the position of the shoulders and the level of the chin;
- Lower your head down until it stops. Then tilt your head back without changing shoulder level. Hold the position for 5 seconds.
The following exercises have been developed to strengthen the neck muscles:
- Put your hand on the back of your head. Tilt your head back, resting on your arm;
- Put your hand in the time zone. As you tilt your head, resist with your hand;
- Put your hand on your forehead, resisting it, tilt your head forward;
- Tilt your head to the side with your right hand and behind your back with your left. Repeat the exercise on the other side.
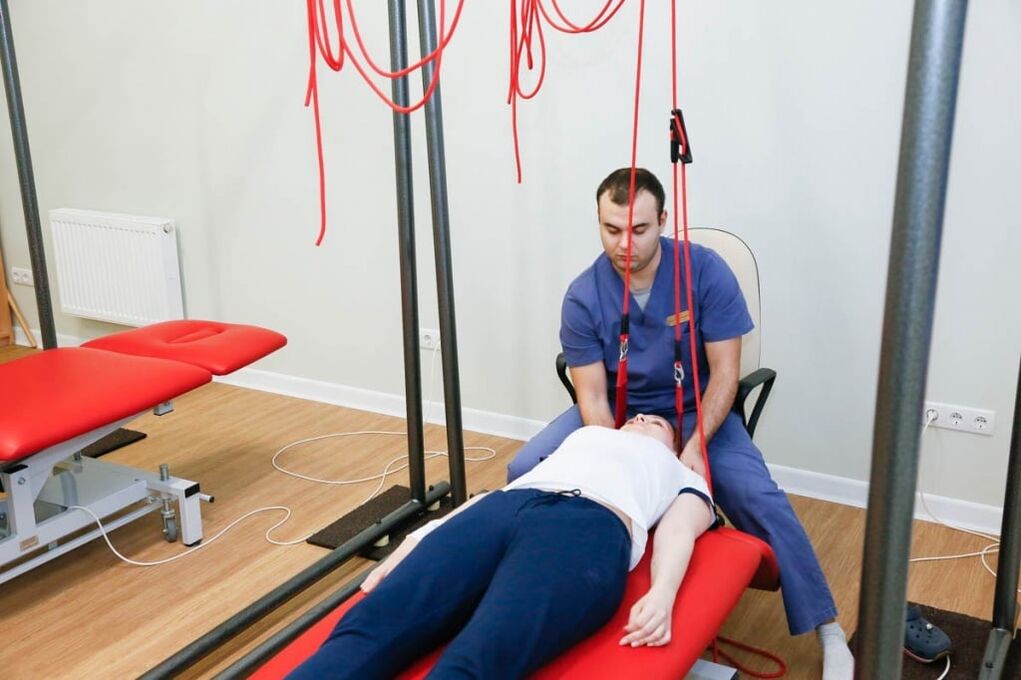
Autogravity therapy is the exact name of the spine procedure. It is performed using special devices. The goal of therapy is to reduce muscle spasm and restore the correct position of the vertebrae. To avoid complications, the treatment of the spine is performed by a doctor.
The following physiotherapeutic procedures are used to improve the blood supply in the pathological focus, alleviate swelling and eliminate pain:
- Diadynamic currents. During this procedure, with the help of a special device, low-frequency currents are applied, which stimulate muscles, relieve cramps and pain. They have a positive effect, improving tissue trophism;
- Ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of UV radiation, the metabolism of vitamin D improves, the calcium content increases, bone tissue strengthens;
- Ultrasound exposure - used to accelerate blood flow, antispasmodic and reparative. Ultrasound is able to penetrate deep into tissues, sometimes used for better absorption of medicinal substances;
- Amplipulse therapy - allows you to relieve pain by blocking nerve impulses from the painful focus.
In the acute period of the disease, which lasts 4-7 days, painkillers, antispasmodics, irritants are used to reduce pain. Peace is assured to the patient. Immobilization of the cervical spine is performed using the Shants collar. Exercise therapy and massage are contraindicated. Apply ultraviolet radiation.
The duration of the subacute period is 29 days. After complete recovery, the patient must rest for a few days. Then you can start a course of rehabilitation therapy. In the chronic course of the disease, the patient is prescribed muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, B vitamins, analgesics - painkillers, NSAIDs. Physiotherapy exercises, massage are provided. The patient is given physiotherapeutic procedures (amplipulses, exposure to alternating current), and the spine is pulled.

Food
Proper nutrition for osteochondrosis is an important condition for achieving remission. The progression of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis is stopped by diet and treatment. Neurologists know how to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, so they make a complex of therapeutic measures, including procedures, exercise therapy, proper diet and lifestyle changes.
Many patients turn to neurologists with the question of how to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and whether there are dietary restrictions. Specialists create individual nutrition programs that take into account the patient's preferences. The osteochondrosis diet is based on a balanced, low-fat diet rich in nutrients. The patient's daily diet includes foods rich in calcium.
How to sleep with cervical osteochondrosis
For patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the question of how to sleep properly with cervical osteochondrosis is relevant. Sleeping on the stomach provokes further development of the disease, so it is better to avoid sleeping in this position. The most optimal positions are the back and hips.
Cervical osteochondrosis progresses while resting on a bed with a soft mattress. Therefore, experts recommend giving preference to elastic mattresses, as well as moderately soft pillows. If a patient is diagnosed with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, experienced experts will tell you which bedding is safe to sleep on.
Prophylaxis
To prevent the onset or progression of cervical osteochondrosis, doctors recommend:
- Maintain proper posture;
- Lead an active lifestyle, take breaks from work;
- Do physiotherapy exercises regularly;
- Sleep on a firm and flat surface, orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- Get rid of bad habits, especially smoking;
- Choose shoes taking into account the physiological structure of the feet;
- Do not carry the bags on one hand, this leads to bending of the spine;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, eat lots of fruits and vegetables;
- He does not sit long with his head bowed;
- Go swimming.
In order to improve blood circulation, massage should be performed regularly.